Roof repair vs. replacement: When is it time?
Built-up and mod-bit roofs

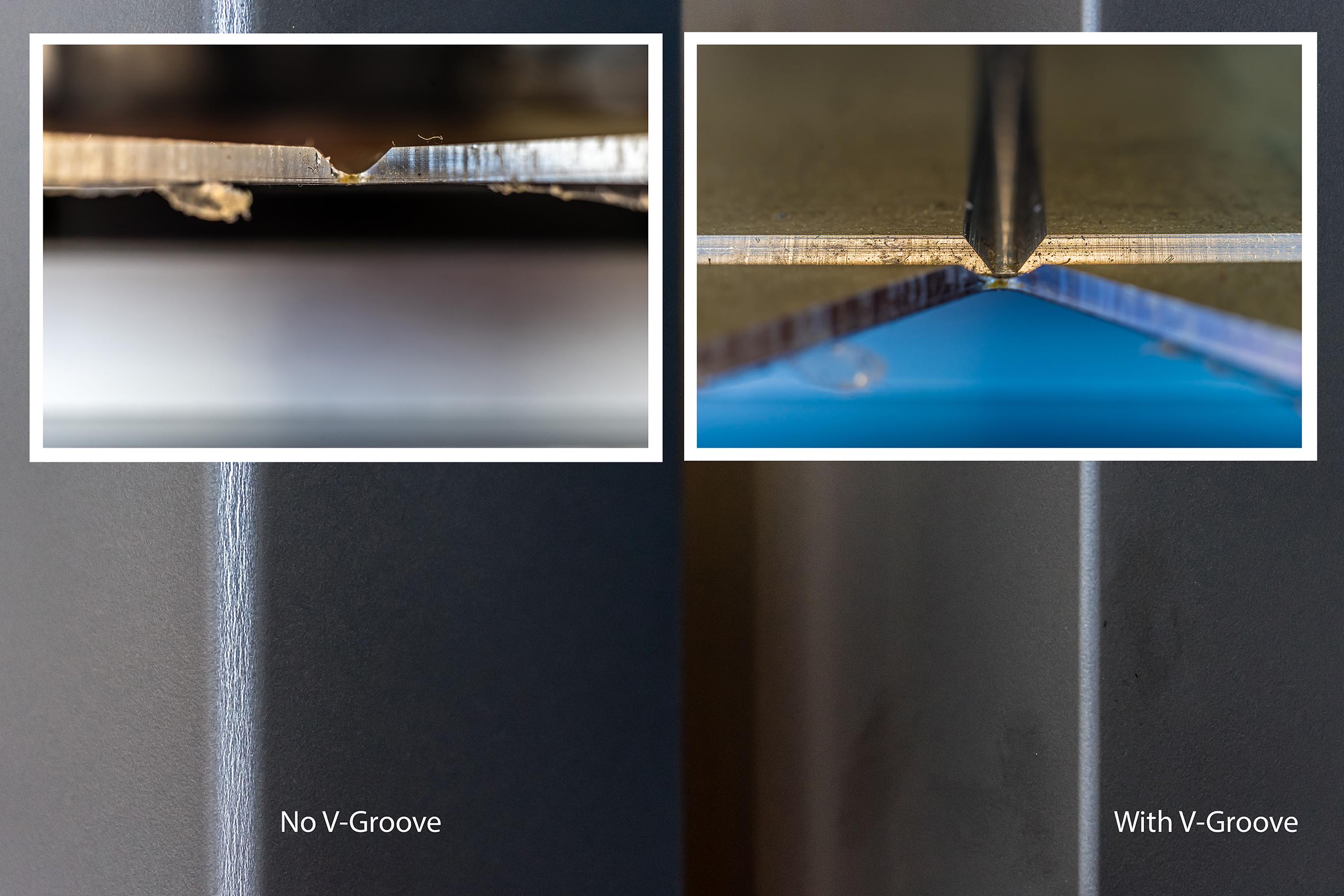
Built-up roofs (BURs) have the longest track record and yield a durable roof. However, they are labour intensive requiring special equipment to install the multiple plies of felt and asphalt. They cannot be installed on steep sloped surfaces and can be difficult to fit around highly detailed roof transitions.
Mod-bit membranes, developed to address asphalt shortages, come in premanufactured rolls of reinforcement coated with styrene-butyl-styrene (SBS) or atactic polypropylene- (APP) modified asphalt. Modified-bituminous membrane roofing is more flexible than traditional built-up and can be applied with hot asphalt, cold adhesive, or a mechanical process, or they may be self-adhered or thermally fused in place. The top surface of a mod-bit roof has a granular surfaced finish with multiple colours available, but they can be bare, embossed with metal, coated, or surfaced with gravel. The bare mod-bit cap sheet would only be used in protected roof assemblies where ultraviolet (UV) protection is not required. The thermally fused applications using a torch have been the largest concern with the application of mod-bit roofs, particularly on buildings in use due to the risk of fire.
Liquid-applied

Historically, liquid-applied roofs have been used as true waterproofing membranes, such as liquid-applied hot rubber over podium decks or liquid urethane in parking garages. Some of the early applications of liquid-applied membranes on roofs were sprayed polyurethane foam (SPF) using acrylic-, silicon-, or urethane-based materials. New products are also being introduced, such as poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyurethane methacrylate (PUMA). The flexibility of these materials and relatively easy application make them excellent choices for difficult-to-access areas and complex roof shapes.
Hybrid roofs

Depending on compatibility of material, various roof membrane components can be used together to achieve performance requirements that may exceed a stock roof membrane. A single-ply membrane can be adhered with a liquid-applied waterproofing material or a mod-bit cap sheet can be installed over built-up plies of felt and asphalt to achieve a premanufactured exposed finish while attaining the redundant durability of the built-up plies. In contrast, an existing smooth roof can be coated with a liquid-applied membrane to restore or improve performance or a mod-bit roof can be surfaced with asphalt and gravel to obtain additional durability and drainage upgrades.
Maintenance to defer future repairs
While regular maintenance is generally understood to be a critical requirement to prolong the life of a roof, it typically does not occur until a leak event occurs and repairs are required to address this deferred maintenance.
Basic housekeeping related to cleaning helps prevent damage to the roof membrane. The roof membrane can be damaged by unwanted vegetation growth, chemical or oil spills, and dead loads directly on the roof membrane. Any activity directly over the roof membrane, such as construction activities or pedestrian access, needs to be avoided to prevent damage. Depending on the duration of the roof activities, protection in the form of catwalks or plywood over insulation should be provided when increased foot traffic is unavoidable.