The noise around acoustics
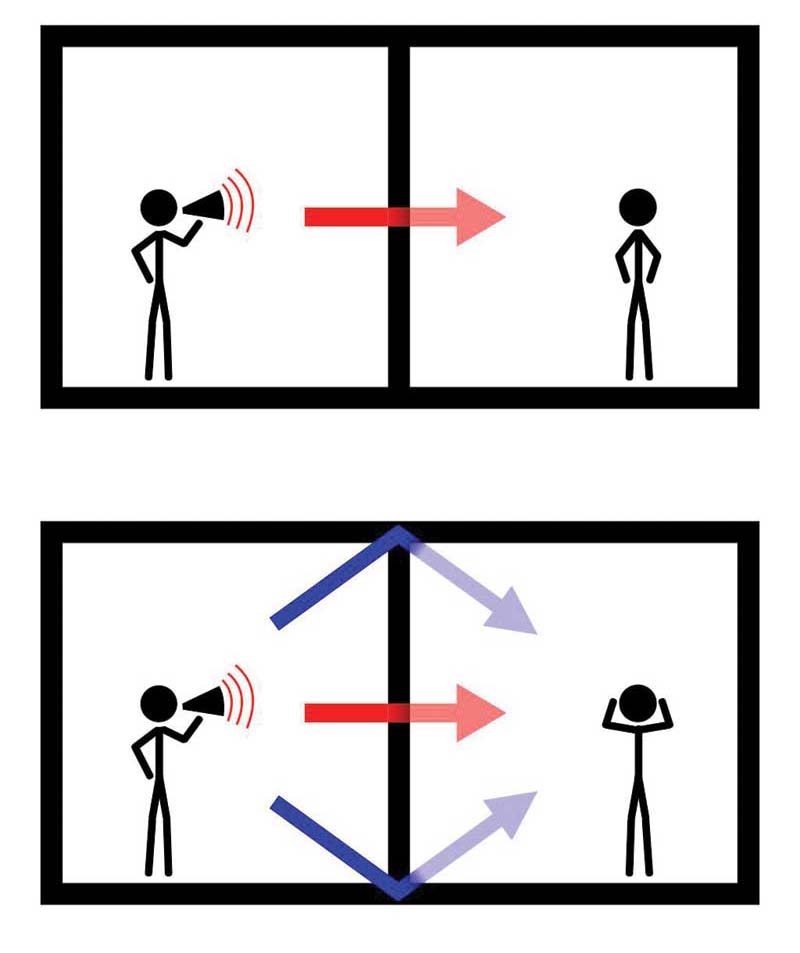
Noise isolation class (NIC) is similar to STC, but is determined by fitting the standard STC contour to one-third octave NR data measured in the field. NIC is a single-number value that approximates the NR of a partition at 500Hz.
Composite sound transmission class
Used to describe the sound transmission properties of a partition with multiple elements, such as a wall with doors and windows, the composite STC (STCc) takes into account the surface area of each element and its transmission loss contribution to the entire assembly.
Apparent sound transmission class
Similar to STC, the apparent sound transmission class (ASTC) value includes the contribution of sound transmitted via flanking paths, such as common flooring, ceiling, structural, and mechanical elements, in addition to sound transmitted directly through the material or partition.
Weighted sound reduction index with spectrum adaptation term
This is a single-number value, in decibels, derived from laboratory transmission loss data (Rw). It is calculated by a curve-fit method similar to STC. Rw puts slightly more emphasis on low-frequency transmission performance of a system than STC and is often combined with a spectrum adaptation term (Ctr)—a single-number value, in decibels, accounting for the characteristics of a particular sound source spectra.
Ceiling attenuation class
The ceiling attenuation class (CAC) is a single-number rating representing a ceiling’s ability to prevent airborne sound from travelling between adjacent spaces when the common wall between those spaces does not extend full-height. It is a good measure for acoustical tile ceilings in closed office spaces with a common ceiling plenum between spaces.
Impact insulation class
A single-number value that describes the ability of a floor/ceiling assembly to reduce impact noise transmission, the impact insulation class (IIC) is determined by fitting a standard contour to one-third octave band sound pressure level data measured under laboratory conditions.
Outdoor/indoor transmission class
The outdoor/indoor transmission class (OITC) is a single-number value that describes an exterior partition’s ability to attenuate outdoor environmental noise. OITC is similar to STC in that it is derived from one-third octave band TL data, but it differs in that it is calculated by mathematical equation, rather than a curve-fit method.
Composite outdoor/indoor transmission class
Employed to describe the sound transmission properties of an exterior partition with multiple elements (e.g. a wall with doors and windows), the composite OITC (OITCc) considers the surface area of each element and its transmission loss contribution to the entire assembly, similar to STCc.
Sound transmission summary
Aside from TL and NR, all these criteria are single-number ratings meant to describe the acoustic behaviour or performance of various systems. However, as sound energy spans a spectrum of low to high frequencies, these ratings do not always tell the whole story and should therefore be used as a general guideline. For high-performance buildings and critical-use spaces, it is important to consider the sound transmission performance of systems across the entire spectrum of audible frequencies.
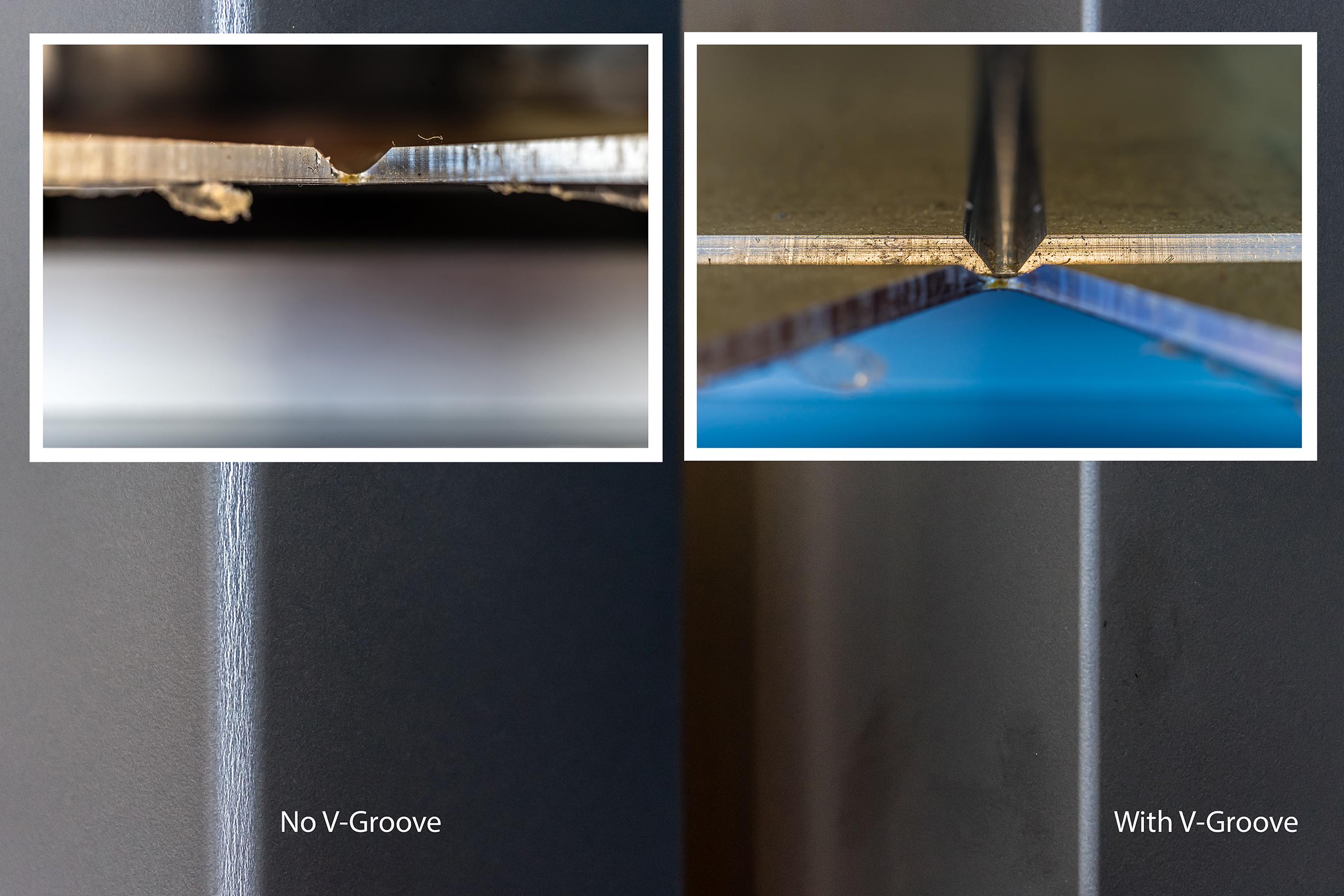
The ability for any construction assembly to mitigate unwanted sound transmission hinges on various factors, such as good workmanship and proper sealing of the wall perimeter and penetrations. Laboratory testing minimizes these types of variables, so it is important they get the same level of attention in the field. As a rule of thumb, if any amount of air can pass through a partition, then sound will be able to more easily transmit through that partition. Even the smallest hole or unsealed penetration can severely degrade the acoustic performance of an otherwise ‘hig-STC’ assembly.