Effective chemical-resistant floor finishes
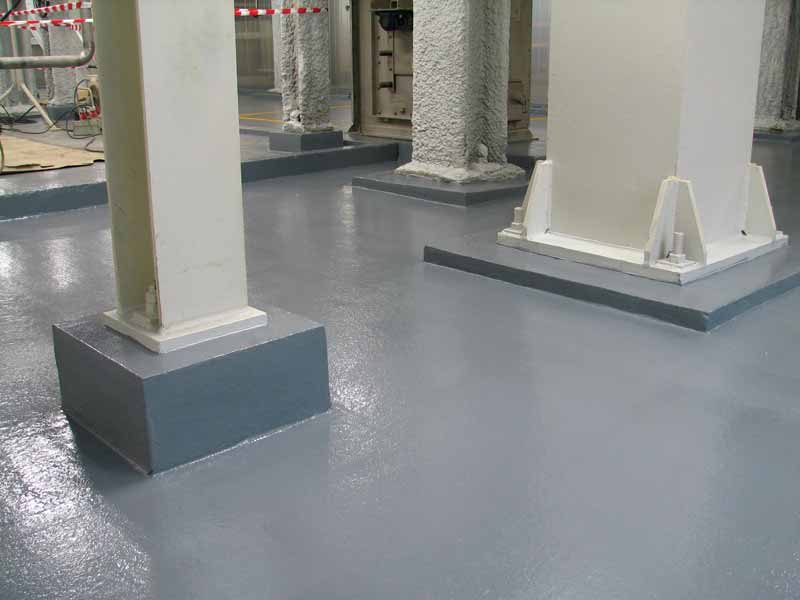

In general terms, all resin flooring is fast curing or hardening as well as tough and abrasion resistant. All tend to produce hardwearing finishes that are chemical-resistant to various degrees, impermeable to liquids, hygienic, and easy-to-clean. They also provide a strong permanent bond to the concrete slab.
However, there are differences between the types of resin flooring materials and product formulations on the market. The following paragraphs outline in basic terms which material is the best fit for a specific situation.
Starting at the thinner end of the scale are water-based epoxies of up to 300 microns. They are typically utilized in light to medium warehousing. These provide excellent dustproofing qualities and are a cost-effective alternative to traditional flooring materials in areas not subjected to rigorous service conditions. These types of solutions have a practical life of two to three years.
Higher build coatings of 300 to 1000 microns are ideal for use in production and processing areas due to the abrasion- and chemical-resistance properties they provide. Quartz aggregates can be incorporated into the finish to create a slip-resistant surface, which is especially useful in areas prone to wet working conditions. The practical life of such systems is three to five years.
Next on the scale are 4 to 6-mm (157 to 263-mils) thick trowel-applied epoxies. These ensure a better level of impact resistance, enabling them to withstand issues such as dropped tools and equipment, point loading from heavily-laden pallets, and the movement of forklift trucks. They are ideal for heavy industry areas (e.g. manufacturing facilities, automotive workshops, and aircraft hangars) placing a lot of demands on the floor. These systems can be specified in a decorative, multicoloured finish, and can be expected to last up to 10 years.
Thick, 4 to 9-mm (157 to 354-mils) cementitious urethane screeds represent a step up in durability and are a common sight in locations where the floor faces heavy impacts, steam cleaning, and thermal shock on a regular basis. This type of floor has anti-slip characteristics, which makes it highly beneficial in sectors such as seafood processing, dairy farming, and breweries. This is a food industry favourite and systems are available that include antibacterial additives to enhance onsite hygiene levels. This type of flooring can last 10 to 15 years even in the most intensive, heavy-duty industrial locations.
Epoxy novolac (EPN) coating systems provide significantly higher chemical- and thermal-resistance properties compared to the bisphenol A-based systems. They have a higher functionality (average reactive groups per molecule) due to switching from bisphenol A backbones to epoxy novolac precursors.
Moreover, this formulation provides the higher cross-link density needed for higher chemical resistance and thermal properties. This includes resistance to concentrated leachate, sulfuric acid, (98 per cent), sodium hydroxide (50 per cent), and biocides.
Coating systems that are 100 per cent solids epoxy novolac floor are ideal for harsh chemical- and solvent-resistant applications. In industrial plants and facilities, they are most commonly found in areas such as secondary containment, solvent storage, pump pads, tank linings, trenches, containment walls, sumps, pits, curbs, and other spaces needing protection from highly corrosive chemicals.
The types of industries that often turn to EPN flooring systems include wastewater and chemical treatment plants, the healthcare sector, electronics, power generation facilities, and textile mills.