Adhering thin-set veneers on multi-storey buildings
Adhered stone veneer bond testing
The Alberta Masonry Council testing investigated the shear bond strength of four popular brands of adhered manufactured stone, with four types of mortar used for the setting bed and with veneers adhered to six different substrates. Adhered manufactured stone veneer units are typically made from lightweight concrete and must weigh less than 0.72 kPa (15 psf) according to ASTM C1670-16, Standard Specification for Adhered Manufactured Stone Masonry Veneer (AMSMV) Units. (For more, read Michael J. Scheffler’s 2001 article, “Thin-stone Veneer Building Façades: Evolution and Preservation,” originally published in APT Bulletin Vol. 32, No. 1.) The substrate is typically a 13-mm (½-in.) mortar embedding a self-furring metal lath. The mortar (i.e. scratch coat) is scored to provide better bond, and is required to be a minimum 13 mm and a maximum 20 mm (¾ in.) according to ASTM C1780-2016a, Standard Practice for Installation Methods for Adhered Manufactured Stone Masonry Veneer. The mortar used to embed the metal lath can be Type N, Type S, or modified.
Exterior-grade cement board is also becoming more common, and is now permitted by ASTM C1780. This replaces the metal lath and mortar scratch coat, but requires the use of a modified dry-set cement mortar compliant with ANSI A118.4, American National Standard Specification for Modified Dry-set Cement Mortar, or ANSI A118.15, American National Standard Specification for Improved Modified Dry-set Cement Mortar. Regardless of the substrate (scratch coat and lath or cement board), Clause 7.2.1 of ASTM C1670 and Clause X1.2 of ASTM C1780 require a shear bond strength of 0.35 MPa (50 psi) using a shear bond test modified from ASTM C482-02, Standard Test Method for Bond Strength of Ceramic Tile to Portland Cement Paste.
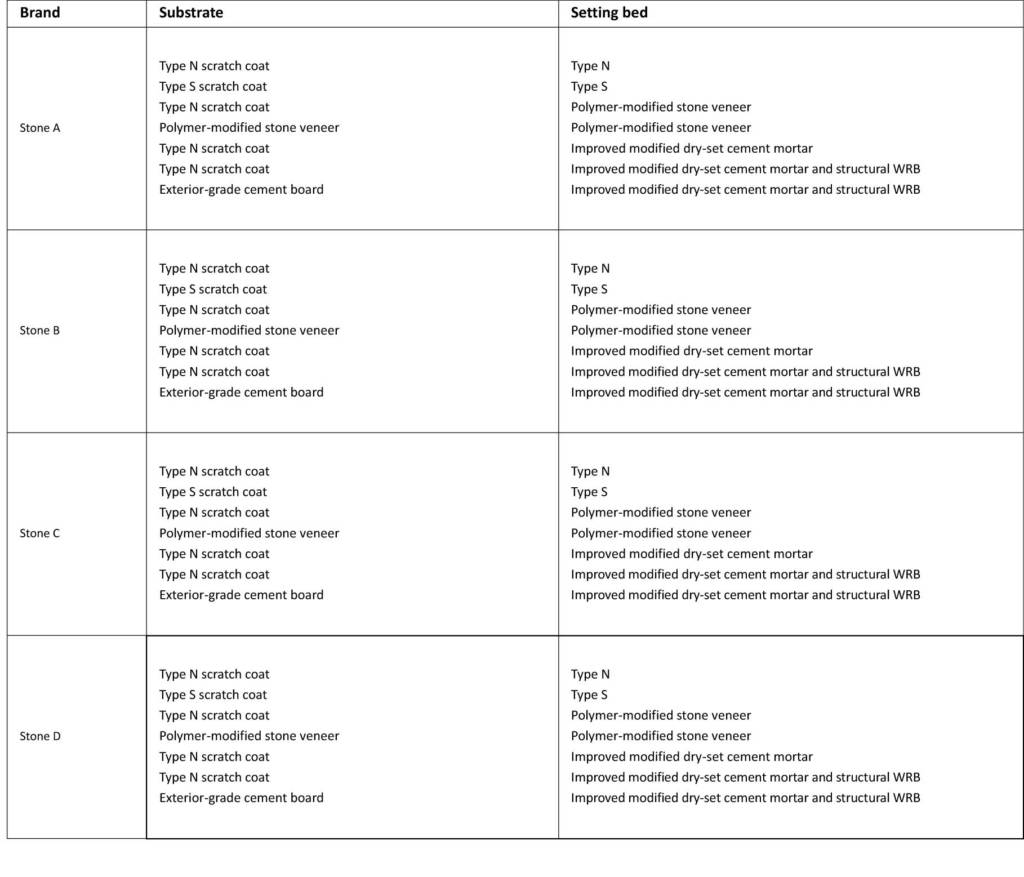
Figure 3 outlines the combinations of stone brand, substrate, and setting bed investigated in the testing program. Shear bond tests of three samples for each combination were completed. The samples consisted of full-size manufactured stone units adhered to a mortar block or cement board substrate and tested according to a modified ASTM C482-02 test. As well, stone veneer units were provided from suppliers, rather than directly from the manufacturers, but the thickness of the manufactured stone samples varied depending on the manufacturer.
Stone samples of approximately 100 x 100 mm (4 x 4 in.) in dimension were cut as needed. The scratched surface was created with a 6-mm (¼-in.) square notched trowel. After the mortar blocks had air-cured for 24 hours (with a typical laboratory temperature of 21 C [70 F] and 25 per cent relative humidity [RH]), a mortar for the setting bed was mixed and applied to the manufactured stone unit sample using a pointed (brick) trowel, or a fluid-applied structural weather-resistant barrier (WRB) was applied to the cured simulated scratch coat and allowed to cure. Cement board substrate samples were constructed using a 13-mm (½-in.) exterior-grade cement board fastened with the manufacturer’s fasteners to a 2×6 wood stud cut to 150 mm (6 in.) in length. A fluid-applied structural WRB was then applied to the cement board and allowed to cure.