A framework for climate resilient performance standard of commercial roofs
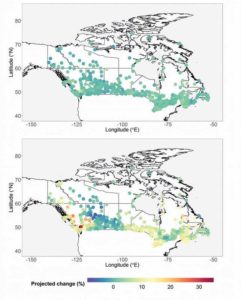
A summary of the projected changes in 1/50 hourly wind pressures at NBC locations is shown in Figure 3 for two extreme levels of projected global temperature increases. The first map shows the projected changes under 0.5 C increase in global temperatures whereas the second one illustrates the projected changes under 3.5 C increase in globally averaged temperatures. From the figure, it is evident extreme wind pressures will change across the NBC locations in the future. More intense changes are projected to occur with larger temperature increases (3.5 C in this case) than smaller rises (0.5 C in this scenario). Overall, the projected changes in 1/50 hourly wind pressures across all NBC locations and under global temperature increases of up to 3.5 C can increase as high as 33 per cent.
Similar to wind, a summary of the projected changes in 1/50 one-day rain at NBC locations is shown in Figure 4 for two extreme levels of future projected global temperature increases. The top panel shows the projected changes under 0.5 C increase in global temperatures whereas the bottom shows the projected changes under 3.5 C increase in globally averaged temperatures. From the figure, it can be seen extreme one-day rainfall is projected to increase across Canada and the magnitude of projected change is higher for larger temperature increases (3.5 C in this case) than smaller ones (0.5 C in this situation). Overall, the projected changes in 1/50 one-day rain across all NBC locations and under global temperature increases of up to 3.5 C were found to range from four to 62 per cent.
Based on the above analysis and in consultation with the roofing community, three climate zone severity classes were defined as normal, severe, and extreme . In the case of wind severity the, ranges are:
- normal (with less than 10 per cent projected change);
- severe (with 10 to 20 per cent projected change); and
- extreme (with greater than or equal to 20 per cent projected change).
The three climate zones for rain severity ranges are:
- normal (with less than 10 per cent projected change);
- severe (with 10 to 40 per cent projected change); and
- extreme (with greater than or equal to 40 per cent projected change).
Finally, the total numbers of NBC locations falling into each of the three climate zone severity classes were established for different degrees of future global temperature increases. These are summarized in Figure 5 where the per cent of total NBC locations (678) falling under each of the three climate zone severity classes are provided. It can be noted more and more NBC locations are projected to switch from normal to severe and extreme classes as the global temperature increases from 0.5 to 3.5 C. It is also determined the switch in climate zone severity classes in the case of extreme rainfall, especially from normal to severe is more drastic and consistent in the case of extreme rainfall than extreme wind. The climate zone severity classes identified for each NBC location and under different levels of future temperature increases were combined with a resiliency index and guidelines for several performance levels. Since the roof systems are designed to last 15 to 20 years, it is recommended climate zone severity classes corresponding to 2 C rise in global temperatures are used as this level of increase is projected to occur around 2050. However, practitioners have the option of choosing classes associated with larger increases in global temperatures in design if they were interested in constructing roof systems for longer time-periods.
The specified slider does not exist.


